Using .NET Aspire to Gate Traffic on Data Availability
Abstract
In cloud-native systems, successful deployment does not guarantee operational correctness.
Applications often start correctly, pass basic health checks, and receive production traffic — even though critical data pipelines have not completed initialization.
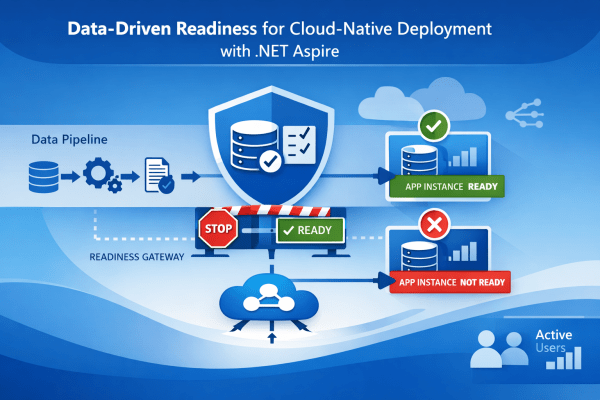
This article presents a data-driven readiness pattern implemented using .NET Aspire, where application instances are marked Not Ready until essential datasets are verified as available and consistent. The approach ensures that traffic is only routed to instances that can produce correct, deterministic results, not merely respond to HTTP requests.
The Problem: “Healthy” Services That Are Not Ready
Modern platforms (Azure Container Apps, Kubernetes, etc.) distinguish between:
- Liveness – Is the process alive?
- Readiness – Can the instance safely receive traffic?
In practice, many systems treat readiness as a shallow check:
- HTTP endpoint responds
- Database connection opens
- Dependency container is reachable
This breaks down for data-dependent services, such as:
- Retrieval-augmented systems
- Agent-based pipelines
- Regulatory or document-driven AI
- Index-backed APIs
If the underlying dataset is empty, stale, or partially initialized, the service may respond — but with incorrect or misleading output.
Continue reading “Engineering Data-Driven Readiness for Cloud-Native Applications”