Creating a fully functional AI Chat App today doesn’t have to take weeks.
With the new Microsoft Agent Framework and .NET Aspire orchestration, you can set up a complete, observable, and extensible AI solution in just a few minutes — all running locally, with built-in monitoring and Azure OpenAI integration.
If you’ve experimented with modern chat applications, you’ve probably noticed they all share a similar design.
So instead of reinventing the wheel, we’ll leverage the elegant Blazor-based front end included in Microsoft’s AI templates — and focus our energy where it matters most: the intelligence and orchestration behind it.
But where things get truly exciting is behind the scenes — where you can move from a simple chat client to a structured, observable AI system powered by Microsoft Agent Framework and .NET Aspire orchestration.
Why Use the Agent Framework?
The Microsoft Agent Framework brings much-needed architectural depth to your AI solutions. It gives you:
- Separation of concerns – keep logic and tools outside UI components
- Testability – verify agent reasoning and tool behavior independently
- Advanced reasoning – support for multi-step decision flows
- Agent orchestration – easily coordinate multiple specialized agents
- Deep observability – gain insight into every AI operation and decision
Essentially, it lets you transform a plain chat app into an intelligent, composable system.
Why .NET Aspire Makes It Even Better
One of the best parts about using the AI templates is that everything runs through .NET Aspire.
That gives you:
- Service discovery between components
- Unified logging and telemetry in the Aspire dashboard
- Health checks for every service
- Centralized configuration for secrets, environment variables, and connection settings
With Aspire, you get orchestration, observability, and consistency across your entire local or cloud-ready environment — no extra setup required.

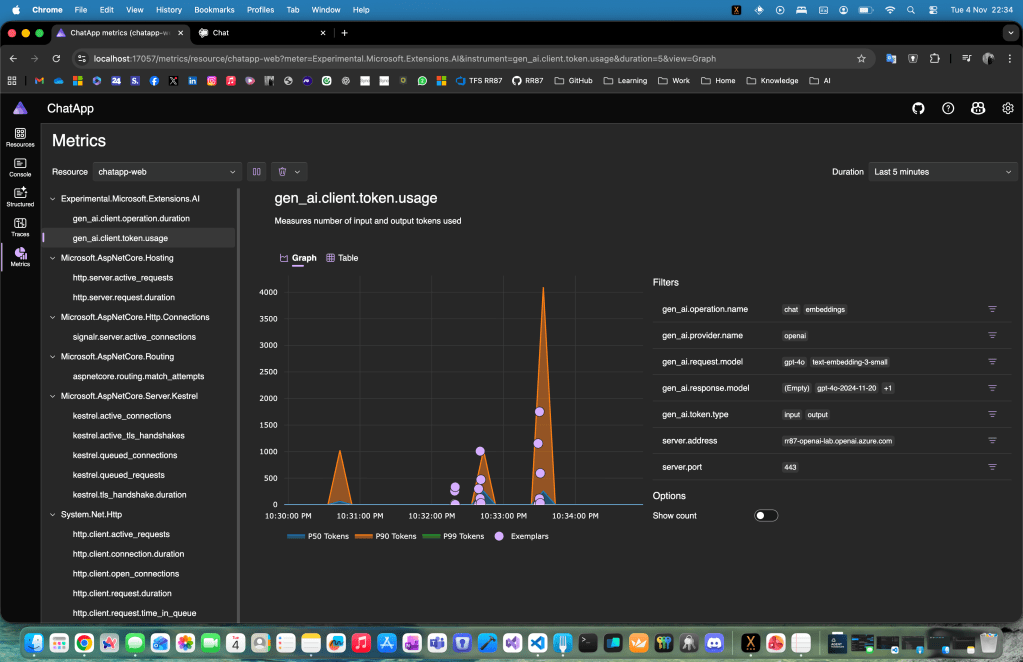
Step 1: Creating the Base Chat App
Start with the AI Chat Web template (aichatweb) from Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Templates.
Then scaffold the Aspire orchestration components for service management and monitoring.
dotnet new install Microsoft.Extensions.AI.Templates
dotnet new aichatweb --Framework net9.0 --provider azureopenai --vector-store local -n ChatApp.Web
dotnet new aspire-apphost -f net9.0 -n ChatApp.AppHost
dotnet new aspire-servicedefaults -f net9.0 -n ChatApp.ServiceDefaults
dotnet sln agent_framework.sln add 02_NET_AI_ChatApp/ChatApp.AppHost/ChatApp.AppHost.csproj
dotnet sln agent_framework.sln add 02_NET_AI_ChatApp/ChatApp.ServiceDefaults/ChatApp.ServiceDefaults.csproj
dotnet sln agent_framework.sln add 02_NET_AI_ChatApp/ChatApp.Web/ChatApp.Web.csprojConfigure your secrets:
dotnet user-secrets init
dotnet user-secrets set "Aspire:Azure:AI:OpenAI:Endpoint" "https://<your-aoai>.openai.azure.com"
dotnet user-secrets set "Aspire:Azure:AI:OpenAI:Key" "<YOUR_KEY>"
dotnet user-secrets set "AzureOpenAI:ChatDeployment" "gpt-4o"
dotnet user-secrets set "AzureOpenAI:EmbeddingDeployment" "text-embedding-3-small"That’s your starting point — a fully functional Blazor AI Chat App integrated with Azure OpenAI and orchestrated by Aspire.
Step 2: Adding the Microsoft Agent Framework
Install the Agent Framework packages:
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Agents.AI" Version="1.0.0-preview.251009.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Agents.AI.Abstractions" Version="1.0.0-preview.251009.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting" Version="1.0.0-preview.251009.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Agents.AI.Hosting.OpenAI" Version="1.0.0-alpha.251009.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Agents.AI.OpenAI" Version="1.0.0-preview.251009.1" />These libraries enable you to host, orchestrate, and monitor AI agents with native .NET dependency injection and telemetry support.
2.1 Create a SearchFunctions Service
To decouple logic from your Blazor UI, define a dedicated class SearchFunctions.cs inside ChatApp.Web/Services.
This service will expose semantic search capabilities as a tool the AI can invoke autonomously.
Why it matters:
- The agent can reason when to call search without embedding logic into UI
- You can unit-test search behavior in isolation
- Tool metadata (via
[Description]) helps the LLM decide when to use it - The framework auto-manages JSON serialization, parameter mapping, and error handling
2.2 Register the Agent in Program.cs
The heart of the setup lies in registering your AI agent through the Agent Framework host extensions:
builder.AddAIAgent("ChatAgent", (sp, key) =>
{
var logger = sp.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Program>>();
logger.LogInformation("Configuring AI Agent with key '{Key}'", key);
var searchFunctions = sp.GetRequiredService<SearchFunctions>();
var chatClient = sp.GetRequiredService<IChatClient>();
var aiAgent = chatClient.CreateAIAgent(
name: key,
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant that gives short, witty answers.",
description: "An AI agent that delivers concise and humorous responses.",
tools: [AIFunctionFactory.Create(searchFunctions.SearchAsync)]
)
.AsBuilder()
.UseOpenTelemetry(c => c.EnableSensitiveData = builder.Environment.IsDevelopment())
.Build();
return aiAgent;
});
builder.Services.AddSingleton<SearchFunctions>();
2.3 Connect the Agent to Your Chat Component
In your Chat.razor, inject the service provider and retrieve your agent:
@inject IServiceProvider ServiceProvider
@using Microsoft.Agents.AI
@code {
private AIAgent aiAgent = default!;
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
aiAgent = ServiceProvider.GetRequiredKeyedService<AIAgent>("ChatAgent");
}
}Now your UI can seamlessly communicate with the configured AI agent.
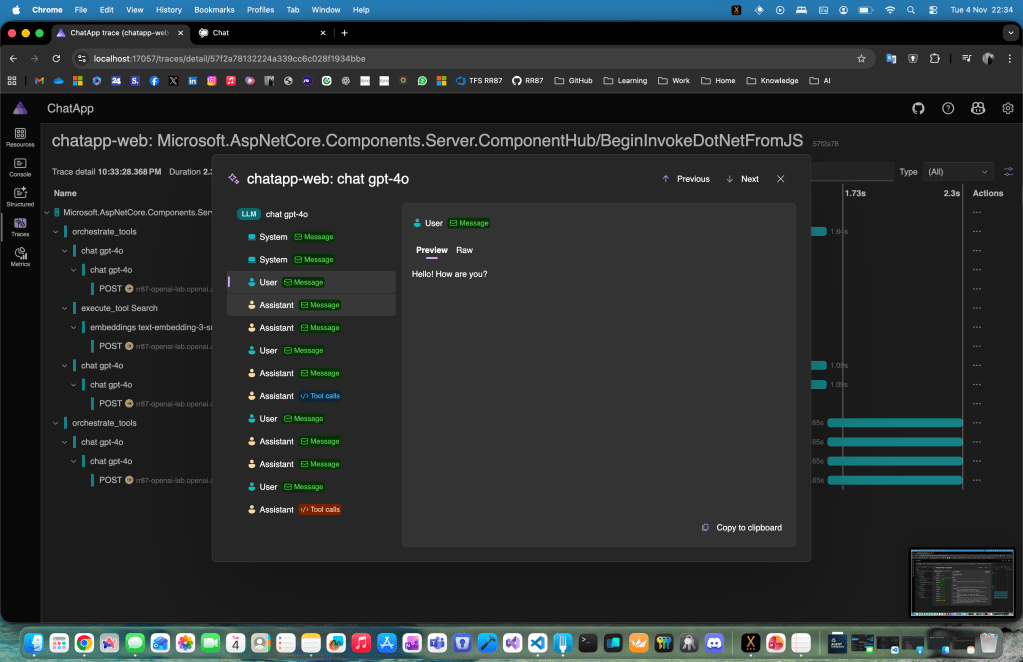
Step 3: Run and Observe with Aspire
When you run the project, the Aspire dashboard launches automatically.
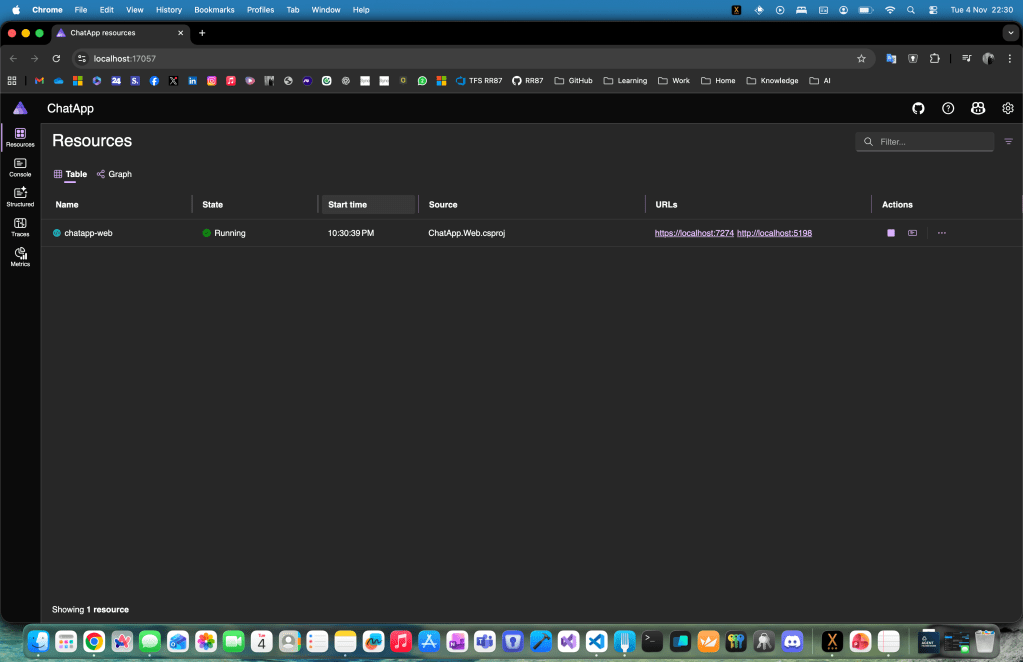
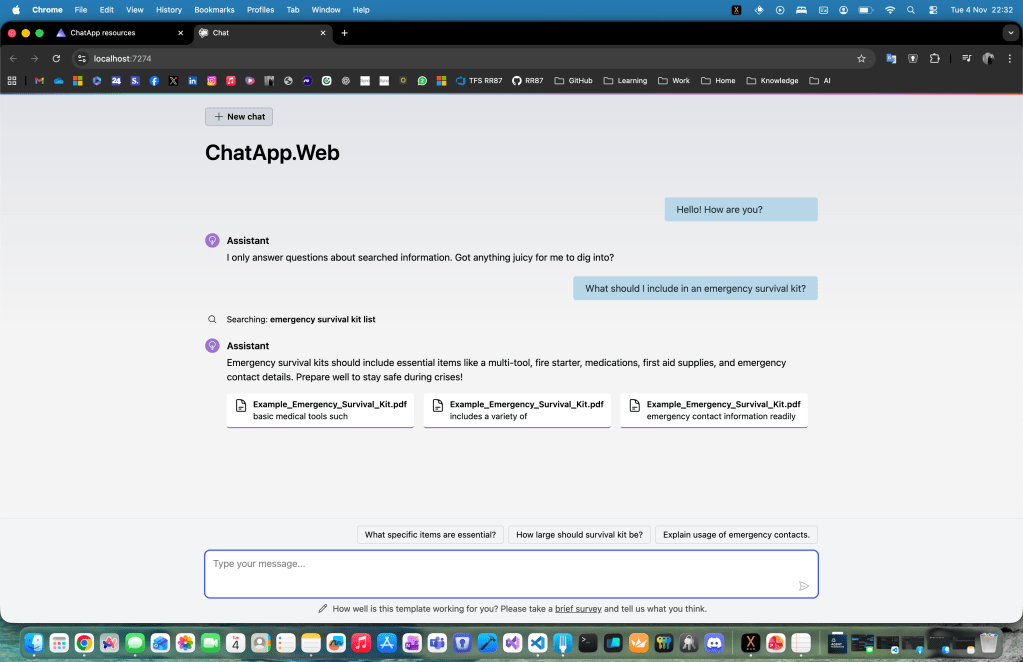
From here, click the web endpoint (for example, https://localhost:7274) to access your chat app.
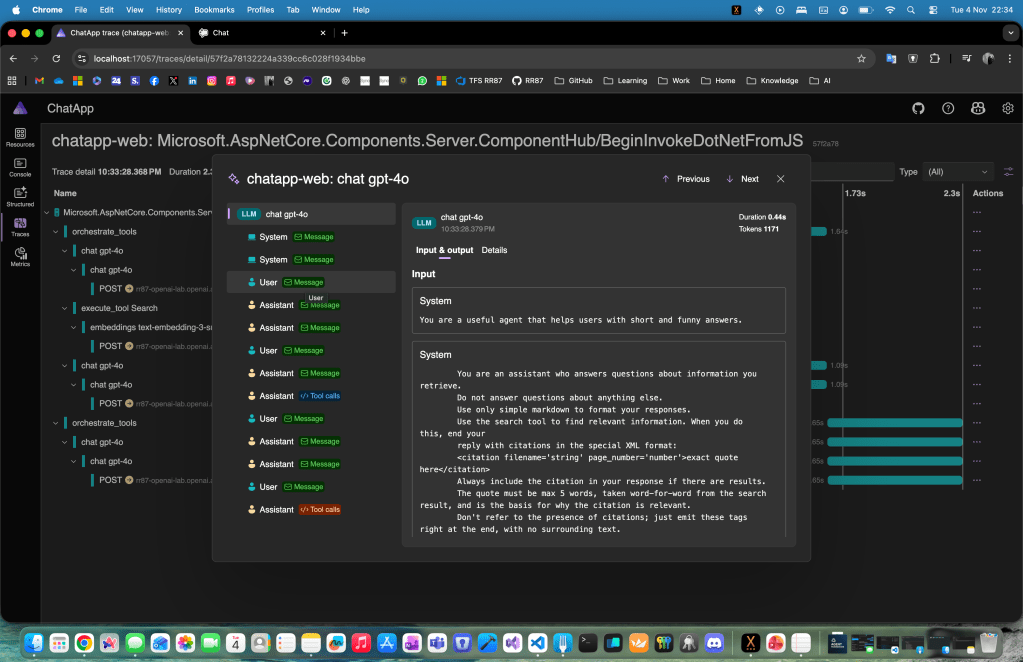
While interacting with your app, open the Metrics and Traces views in Aspire. You’ll see in real-time how:
- The agent triggers the search function
- It sends and receives tokenized data
- It assembles responses based on retrieved context

What’s Next: Advanced Scenarios
This example only scratches the surface. In upcoming articles, we’ll explore:
- Extending your agent with multiple tools
- Multi-agent collaboration
- Custom middleware for pre/post processing
- Recommended design patterns and practices
- Deploying to Azure with Aspire’s one-command provisioning
Final Thoughts
This project shows how, in just minutes (or a few focused hours), your team can stand up a fully functional AI Chat App — capable of reading and reasoning over your internal documentation, surfacing references, and presenting them right in context.
No need to fuss over UI; focus on the AI logic, and deploy everything to Azure with a single click.
That’s all folks!
Cheers!
Gašper Rupnik
{End.}


Love the content Gašper 💪👌